
Multi-Vector microgrid
The Multi-Vector microgrid platform enables the implementation of several energy management laws to control power flows in multi-load multi-source AC and DC microgrids, combining different energy vectors such as hydrogen, electricity and heat. These microgrids are built around specific architectures allowing the connection of different autonomous generators, consumers, renewable energy sources as well as different storage systems.
Depending on the presence or absence of a communication network, different classes of energy management algorithms can be implemented. We can thus differentiate between microgrids with communication networks between producers and consumers (centralized or distributed management) or without a communication network (decentralized management).
The main objectives revolve around the research of optimal power architecture taking into account energy efficiency and network quality, but also durability, availability and reliability. The platform gathers 3 main activities:
- Sizing of autonomous power systems
- Electrical energy management and stabilization
- Reliability and diagnosis
Specificities
- Multi-source and multi-vector networks: Electricity, heat and hydrogen
- Centralized, distributed and decentralized energy management
- Massive integration of renewable energies in microgrids
Application sectors
- Energy
- Aerospace industry
- Automotive Industry / Mobility
- Railway industry
- Shipbuilding industry
Keywords
- Energy efficiency
- Dynamic performance
- Dynamic stability
- Renewable Energy (RE)
- Centralized/distributed/decentralized control
- Smart microgrid
- Reliability
- Availability
Mutualization of energy storage systems in a general context of energy management of a multi-vector network (electricity, H2, heat)
Development of the technological elements of interconversion and management elements :
- Hydrogen” electrical network
- Heat and Electricity
- Hydrogen and Heat
Distributed management of multi-vector microgrid
- Power flow management: Consensus approach, multi-agent, etc.
- Optimization
Power electronics and close control of electrical conversion systems
- Specific power electronics,
- Robust control,
- Parameter estimators, state observers,
- Diagnosis and prognosis
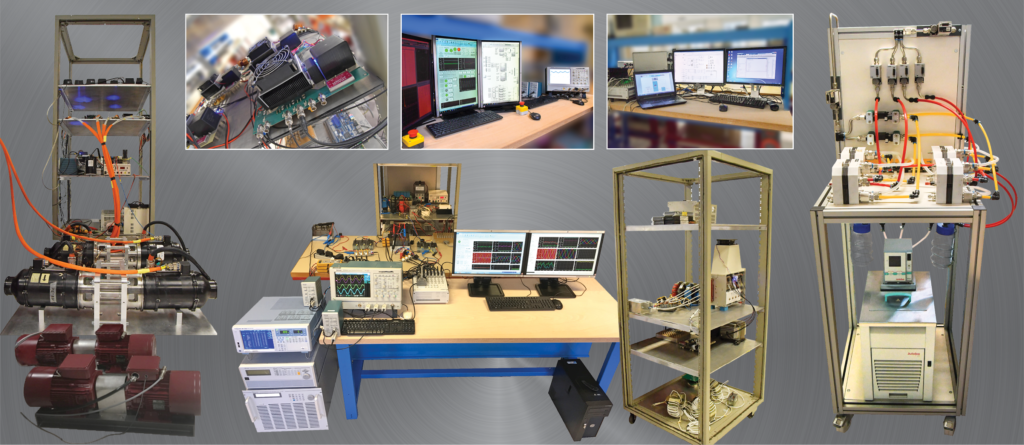
- DC grid simulator +/-20 kW
- Static converters with wide-gap components
- AC grid simulator AC +/-30 kW
- Real time Simulator Power HIL with PXI device of National Instrument and eHS sover from OPAL-RT
- Supervision/control system
- Real-time systems from dSPACE for rapid control prototyping for the implementation of energy management algorithms
- Precision power analyser
- AC/DC Electronic loads
- AC/DC sources
- Three-phase electric generators + variable speed drives

Development of a “Fuel Cell Management System”
Development of energy management systems dedicated to fuel cells and electrolysers connected to a DC microgrid. The objective is to optimize the durability of electrochemical systems by adapting the electrical stresses seen by each cell.
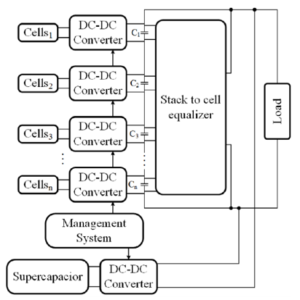
Internal architecture of the PAC system developed
Distributed Energy Management in AC microgrids
Optimized and distributed management of energy flows in an AC microgrid without a communication network between producers and consumers. The management algorithms developed allow to ensure an equal distribution of power flows between generators while taking into account network quality constraints.
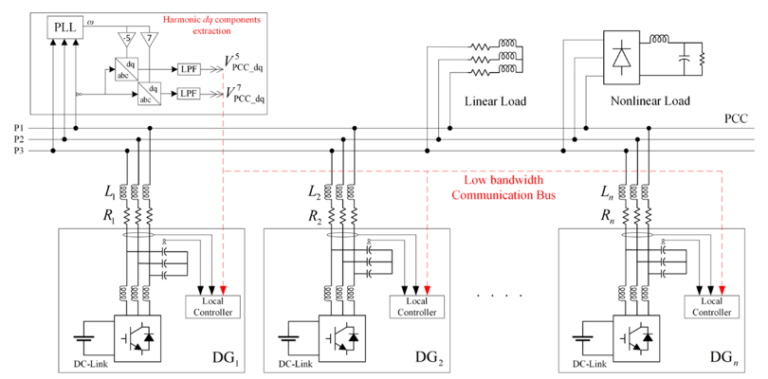
Typical electrical architecture of the studied AC microgrids
Study of power and control architectures of sources and loads connected to avionics DC microgrids
The major technological revolution in new aircraft is based on intensive electrification of many aircraft components and on the fact that the speed of electrical generators is becoming variable. The architecture developed makes it possible to ensure dynamic stability when seeking a compromise between energy efficiency, compliance with standards and compactness.
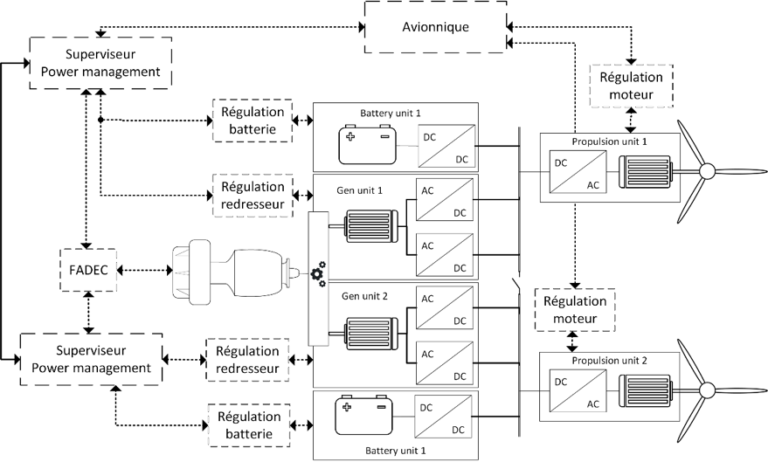
Avionics electrical grid architectures and controls
Jean-Philippe Martin
Jean-Philippe.martin@univ-lorraine.fr
+33 (0)3 72 74 42 58
LEMTA
2 avenue de la Forêt de Haye
BP 90161
54505 VANDOEUVRE-LÈS-NANCY CEDEX